说明:本系列博客用来记录本人在学习minisam过程中的理解,方便同大家一起谈论。
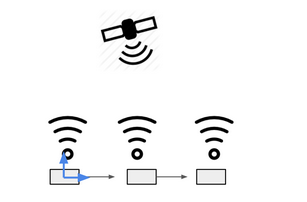
1、含有类似gps测量的位姿问题
如图所示,是一个含有类似gps-like factor的二维问题,我们依然使用因子图对其进行求解。
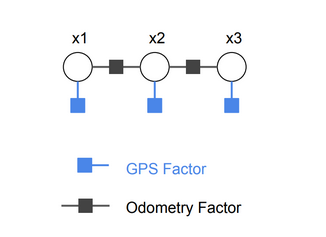
我们定义系统状态变量,其中。
本次例程共有二种类型的因子:(1)binary odometry factors;(2)GPS-like factors。用因子图来表示问题模型为:
如果定义类似gps测量因子是服从高斯分布的,则因子的概率分布为:
其中,是高斯分布的测量协方差,误差函数为:
误差函数的雅克比矩阵为:
2、c++程序分析
查看所有源程序(含有自己写的中文注释),点击这里源代码链接
- 定义gps因子类。
// 定义gps因子类
class GPSPositionFactor : public Factor {
private:
Eigen::Vector2d p_;
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
GPSPositionFactor(Key key, const Eigen::Vector2d& translation,
const std::shared_ptr<LossFunction>& loss)
: Factor(1, std::vector<Key>{key}, loss), p_(translation) {}
virtual ~GPSPositionFactor() = default;
// make a deep copy
std::shared_ptr<Factor> copy() const override {
return std::shared_ptr<Factor>(new GPSPositionFactor(*this));
}
// 误差 = y - exp(m * x + c);
Eigen::VectorXd error(const Variables& variables) const override {
const Sophus::SE2d& pose = variables.at<Sophus::SE2d>(keys()[0]);
return pose.translation() - p_;
}
// 雅克比矩阵
std::vector<Eigen::MatrixXd> jacobians(
const Variables& /*values*/) const override {
Eigen::MatrixXd J(2, 3);
// clang-format off
J << 1, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0;
// clang-format on
return std::vector<Eigen::MatrixXd>{J};
}
// optional print function
void print(std::ostream& out = std::cout) const override {
out << "GPS Factor on SE(2) on " << keyString(keys()[0]) << std::endl;
}
};
- 创建因子图框架,加入里程计因子和gps因子。
// 因子图容器
FactorGraph graph;
// 里程计测量的误差函数
const std::shared_ptr<LossFunction> odomLoss = ScaleLoss::Scale(1.0);
// 加入里程计因子
// 在连续位姿之间加入里程计因子
graph.add(BetweenFactor<Sophus::SE2d>(
key('x', 1), key('x', 2), Sophus::SE2d(0.0, Eigen::Vector2d(5, 0)),
odomLoss));
graph.add(BetweenFactor<Sophus::SE2d>(
key('x', 2), key('x', 3), Sophus::SE2d(0.0, Eigen::Vector2d(5, 0)),
odomLoss));
// gps测量因子误差函数, 二维
const std::shared_ptr<LossFunction> gpsLoss =
DiagonalLoss::Sigmas(Eigen::Vector2d(2.0, 2.0));
// 加入gps因子
// note that there is no prior factor needed at first pose, since GPS provides
// the global positions (and rotations given more than 1 GPS measurements)
graph.add(GPSPositionFactor(key('x', 1), Eigen::Vector2d(0, 0), gpsLoss));
graph.add(GPSPositionFactor(key('x', 2), Eigen::Vector2d(5, 0), gpsLoss));
graph.add(GPSPositionFactor(key('x', 3), Eigen::Vector2d(10, 0), gpsLoss));
graph.print();
cout << endl;
- 加入变量初始值和随机噪音
// 加入变量初始值和随机噪音
// add random noise from ground truth values
Variables initials;
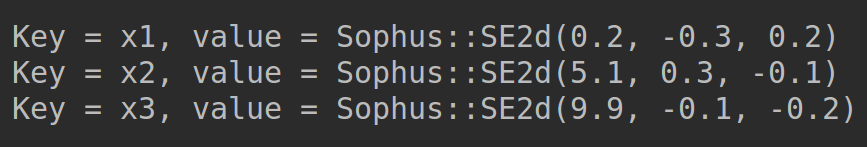
initials.add(key('x', 1), Sophus::SE2d(0.2, Eigen::Vector2d(0.2, -0.3)));
initials.add(key('x', 2), Sophus::SE2d(-0.1, Eigen::Vector2d(5.1, 0.3)));
initials.add(key('x', 3), Sophus::SE2d(-0.2, Eigen::Vector2d(9.9, -0.1)));
initials.print();
cout << endl;
- 使用LM优化方法进行优化
// 使用LM优化方法对初始值进行优化
LevenbergMarquardtOptimizerParams opt_param;
opt_param.verbosity_level = NonlinearOptimizerVerbosityLevel::ITERATION;
LevenbergMarquardtOptimizer opt(opt_param);
Variables results;
auto status = opt.optimize(graph, initials, results);
if (status != NonlinearOptimizationStatus::SUCCESS) {
cout << "optimization error" << endl;
}
results.print();
cout << endl;
- 计算边际协方差(误差)
// 计算所有位姿的边际协方差
MarginalCovarianceSolver mcov_solver;
auto cstatus = mcov_solver.initialize(graph, results);
if (cstatus != MarginalCovarianceSolverStatus::SUCCESS) {
cout << "maginal covariance error" << endl;
}
Eigen::Matrix3d cov1 = mcov_solver.marginalCovariance(key('x', 1));
Eigen::Matrix3d cov2 = mcov_solver.marginalCovariance(key('x', 2));
Eigen::Matrix3d cov3 = mcov_solver.marginalCovariance(key('x', 3));
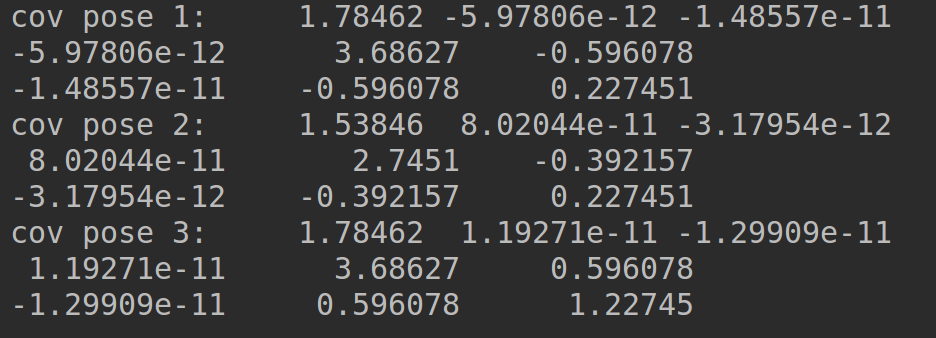
cout << "cov pose 1:" << cov1 << endl;
cout << "cov pose 2:" << cov2 << endl;
cout << "cov pose 3:" << cov3 << endl;
return 0;
三、代码运行结果分析
显示初始值:
进行优化,显示优化结果:
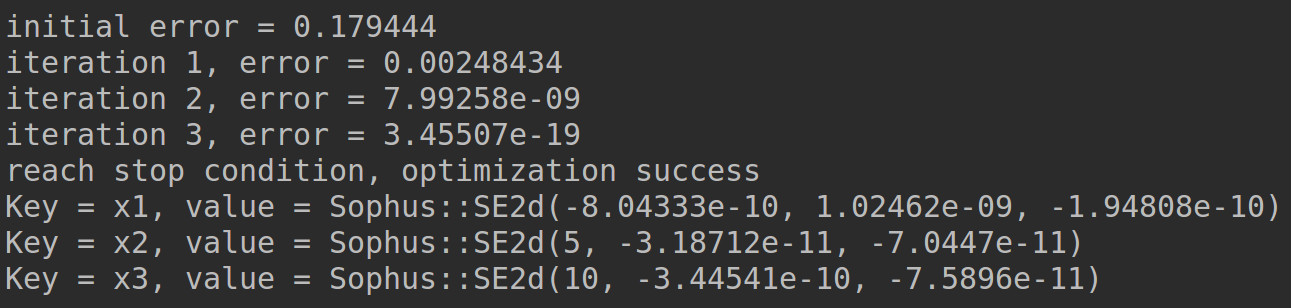
边际协方差: